What is Fabric Water Vapor permeability?
The Water Vapor permeability test of textile fabrics is mainly to test the Water Vapor permeability of fabrics under different temperature and humidity. It is to simulate the ability of textile fabrics to transfer the body to naturally discharge water vapor to the external environment after simulating the sweating state of the human body under different activities. Water Vapor permeability is the quality or efficiency of water vapor transmitted on both sides of the fabric; the assessment is the flow of water vapor, which comes from the water vapor emitted by the human body during exercise, and is also affected by the water vapor in the external environment.
Characteristic index of Water Vapor permeability
- Water vapor transmission rate (WVT)
When both sides of the sample are maintained at the specified temperature and humidity conditions, the mass of water vapor passing through the unit area of the sample vertically within the specified time is expressed in grams per square meter per hour (g/(m2 h)) or grams per square meter for 24 hours (g /(m2·24 h) is the unit.
- Water vapor permeability (WVP)
Under the condition of maintaining the specified temperature and humidity on both sides of the sample, under the unit water vapor pressure difference, the mass of water vapor passing through the unit area of the sample vertically within the specified time, in grams per square meter Pascal hour (g/(m2·Pa·h) ) as the unit.
- Waterpermeability coefficient
Under the condition of maintaining the specified temperature and humidity on both sides of the sample, under the unit water vapor pressure difference, the mass of water vapor vertically penetrating through the unit thickness and unit area of the sample per unit time, expressed in grams centimeters per square centimeter second Pascal (g cm/ (cm2·s·Pa)) as the unit.
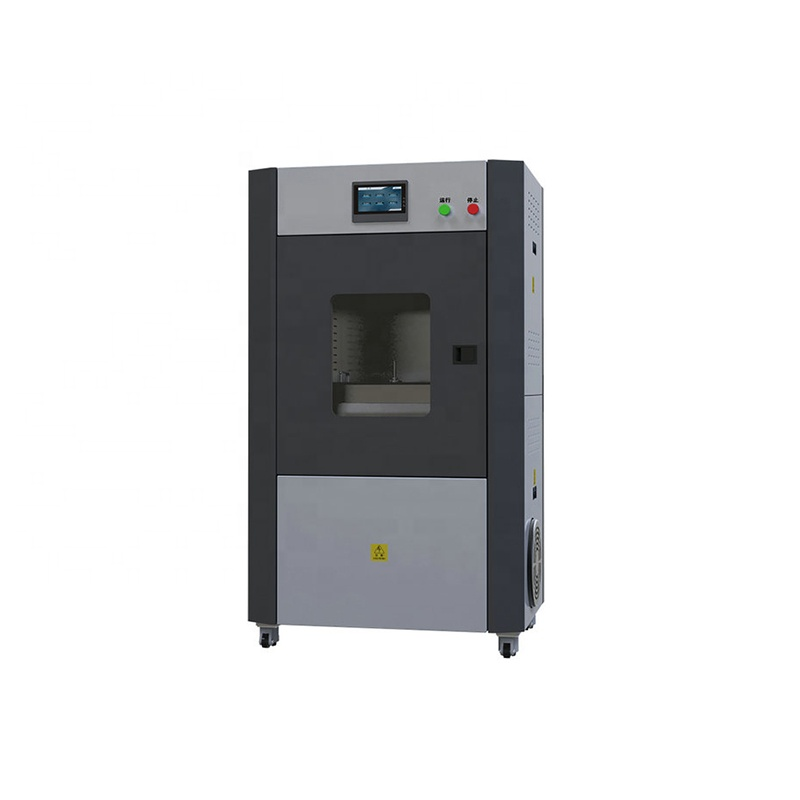

ASTM E96 Automatic Textile Fabric Moisture Permeability Tester
Common test methods at home and abroad for water permeability
- Moisture absorption (desiccant) method
Dry the desiccant (anhydrous calcium chloride) particles (0.63-2.5) mm in an oven at 160°C for 3 hours to keep the desiccant 100% dry. Then put about 35g of the cooled desiccant into the test cup, and shake it evenly, so that the desiccant becomes a plane and its surface is about 4mm lower than the sample. Then put the sample test face up, place it on the test cup, put the gasket pressing piece, and tighten the nut. Then use vinyl tape to seal the sample gasket and pressure ring from the side to form a sample assembly. Place the positive cup of the sample assembly in the test instrument; after 1 hour of test humidity adjustment time, take it out, put it in a desiccator to balance for half an hour, weigh it, and then put it into the instrument for a period of time according to the standard or agreed test time After a period of time, weigh again. The weight difference of the second weighing is used in the formula to obtain the moisture permeability of the sample. The main standards are GB/T 12704.1, ASTM E96 method A/C/E, JIS L 1099 A-1.
- Evaporation (positive cup water method) method
Use a graduated cylinder to inject water at the same temperature as the test condition; the amount of water used is in accordance with the requirements of each standard. Put the test sample on the test cup; place the cup in the test instrument; weigh after a period of balance to obtain the initial weight, and then weigh again after a period of testing. The mass difference of the second weighing is used in the formula to obtain the moisture permeability of the sample. The main standards are: GB/T 12704.2 method A, ASTM E96 method B/E, JIS L1099 A-2, BS 7209.
- Evaporation (inverted cup of water method) method
Use a graduated cylinder to inject water at the same temperature as the test condition; the amount of water used is in accordance with the requirements of each standard. Put the test sample on the test cup; invert the cup and place it in the test instrument; weigh after a period of balance to obtain the initial weight, and then weigh again after a period of testing. After calculation, the moisture permeability of the sample was obtained. The main standards are: GB/T 12704.2 method B, ASTM E96 method BW.
- Potassium acetate method
Inject saturated potassium acetate solution into the test cup, about 2/3 of the height of the cup; then seal the sample at the test cup and place it upside down in the test water tank. Weigh the overall mass of the test cup before the test and the overall mass of the test cup after 15 minutes. The main standards are: JIS L1099 method B-1, JIS L1099 method B-2, ISO 14956.
Comparison of water permeability test methods in various countries
Commonly used water permeability standards are national standard, European standard, American standard, and Japanese standard. These standards have moisture absorption method and evaporation method respectively, but the test conditions used in these standards are not consistent, so the measured results are also inconsistent. So, how to choose?
Generally, the standard of that region is adopted according to which region the product is to be sent to. However, since the United States has always been in a leading position in this industry, and the market in this country is also very large, the data tested by this method is also relatively high. ASTM standard Naturally, it becomes the most commonly used method. Most customers are now using this method for testing. Finally, choose the moisture absorption method or evaporation method according to the characteristics of the sample.
The main factors affecting the test results
When doing water permeability tests, it often happens that the same batch of fabrics, fabrics and garments are tested by different inspection agencies or tested by the same agency at different times, and the results vary greatly.
At present, there are many methods for testing the water permeability of textile fabrics at home and abroad. In daily life, brand sportswear will have waterproof and Water Vapor permeability indicators, but generally there is no specified testing method. At present, the results of various common test methods are not relevant and comparable. Therefore, to evaluate the water permeability performance of clothing, the first thing to determine is the test method. After determining the test method, attention should be paid to the various influencing factors mentioned in this article to ensure the repeatability of the test results.
- The influence of desiccant
(1) Uniformity of particle size distribution of calcium chloride
The specifications of calcium chloride will directly affect its moisture absorption effect. The national standard stipulates that the particle size of calcium chloride is (0.63-2.5) mm, and it is stipulated that after the environment is balanced, the calcium chloride should be shaken up and down evenly. The purpose is to Prevent the deliquescence of calcium chloride from affecting the test results.
Calcium chloride has strong moisture absorption effect, the finer the particles, the larger the specific surface area and the faster the moisture absorption speed, but after it absorbs moisture and deliquesces, it will form a protective layer of calcium chloride hexahydrate on the surface. The easier it is to form a protective layer in the wet stage, the easier it is to prevent the hygroscopicity of the internal calcium chloride in the subsequent formal test stage, which affects the test results.
Before the test, it is necessary to control the particle size of the purchased desiccant with a specified sieve, and to maintain the uniformity of particle distribution as much as possible during the filling process.
(2) The dosage of calcium chloride
The national standard has clear regulations on the amount of calcium chloride, about 35g, and the distance between the sample surface and the desiccant should be about 4mm, and the surface of the desiccant should be flat. This can effectively control the consistency of the air layer between the sample and the desiccant. The size of the air layer determines the total amount of moisture in the air layer. When the desiccant is working, it first dries the moisture in the air layer in the sample assembly to make it 100% dry, and forms a pressure difference of water vapor with the outside of the sample. . The height of the air layer determines the height and path of water vapor transmission. If the desiccant is not a flat surface, the sample will be damp during the test and will sag. If the desiccant is in direct contact with the fabric, water vapor will form a layer on the contact surface. Direct access to the experimental assembly has a greater impact on the test results.
During the test, the amount of desiccant used and its surface level in the sample cup should be strictly controlled.
- The influence of adjustment time in the evaporation method
In the same environment, after the test is adjusted for 0.5h and 1h, and the test time is 2h, the test results will have different differences due to different fabric styles. Therefore, it is suggested that the test adjustment time should be 1h.
- The influence of wind speed
(1) The difference in wind speed on the surface of different test cups with the same equipment
At present, there are many manufacturers of water permeability testers, and the number of sample cups that can be accommodated by different instruments is different. Some instruments can accommodate eight at the same time. If the sample cups in the box cannot move horizontally at a certain speed, it will be difficult to keep the wind speed on the surface of the sample cups consistent, which will directly affect the test results of parallel test samples and cannot be parallelized. Such test results are not acceptable, and the instrument needs to be repaired and calibrated to ensure the consistency of the test results of parallel samples.
(2) Differences in air supply methods between different devices
Some of the water permeability testers currently on the market adopt the design of parallel air supply by horizontal impellers; some use fan air supply. The horizontal air supply system makes the wind on the same horizontal plane, so that the surface wind speed of each sample can be consistent. In the fan air supply system, it is difficult to achieve a consistent surface wind speed for each sample.
- Still air layer
In the positive cup method test, the evaporation of the test water must first pass through the still air layer; and the still air layer will have a certain moisture resistance, which has a greater impact on the water permeability test results. Therefore, Appendix B of GB/T 12704.2 stipulates the method of eliminating the influence of still air layer and correcting the test results. Then during the test, we need to use a test cup that is consistent with the standard and put in the test water volume specified in the standard. In order to keep the still air layer in the cup consistent, so as to ensure the consistency of the test results of parallel samples.
- The tightness between the sample and the test cup
In testing the poured glass method, the tightness of the sample is very important. If the sealing is poor, the moisture in the cup will leak from the edge, or wet the surface of the sample from the edge, thereby evaporating and losing. Such test results are not acceptable and should be avoided.
- Test the validity of the sample
The sample should be representative, no creases or holes are allowed in the sample, and the coated fabric should not have obvious thickness unevenness, blistering, etc. The test surface of the specimen must be oriented correctly.